This page has some hints about debugging the engine.
See also [Crashes](Crashes.md) for advice on handling engine crashes (specifically around obtaining stack traces, and reporting crashes in AOT Dart code).
## Running a Flutter app with a local engine
First, make sure the appropriate version of the engine is built (see [Compiling the engine](./contributing/Compiling-the-engine.md)).
### Using the Flutter tool
Run your Flutter app with:
```bash
flutter run --local-engine=XXXX --local-engine-host=YYYY
```
to run an app with the local engine where `XXXX` should be replaced with the version you wish to use. For example, use `--local-engine=android_debug_unopt --local-engine-host=host_debug_unopt` to run a debug android engine or `--local-engine=ios_debug_sim_unopt --local-engine-host=host_debug_unopt` to run a debug iOS simulator engine.
> 💡 **TIP**: When developing on a Mac with ARM (M CPU), use `--local-engine-host=host_debug_unopt_arm64`.
>
> You can continue to use `host_debug_unopt` (required for Intel Macs), but the engine will be run under Rosetta
> which may be slower. See [Developing with Flutter on Apple Silicon](../platforms/desktop/macos/Developing-with-Flutter-on-Apple-Silicon.md)
> for more information.
It is important to always have a `host_XXXX` version of the engine built when using a local engine since Flutter uses the host build's version of Dart.
### Using Visual Studio Code
You will need to add a new [launch configuration](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/debugging#_launch-configurations) in the `launch.json` file:
```json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Launch (local engine)",
"request": "launch",
"type": "dart",
"args": ["--local-engine", "XXX", "--local-engine-host", "YYY"]
}
// Other profiles below..
]
}
```
## Bisecting a roll failure
If the engine roll is failing (see [Autorollers](../infra/Autorollers.md)), you can use `git bisect` on the engine repo to track down the offending commit, using the `--local-engine` and `--local-engine-host` arguments as described above to run the failing framework test with each version of the engine.
## Tracing OpenGL calls in Skia
All OpenGL calls in Skia are guarded by either the `GR_GL_CALL_NOERRCHECK` or `GR_GL_CALL_RET_NOERRCHECK` macros. Trace events may be added in these macros to trace all GL calls made by Skia, for example [in a patch like this](https://gist.github.com/chinmaygarde/607eb86d5447615b9cf2804a4f8fb1ce).
Due to the number of events traced to the timeline, the trace buffer may be filled up very quickly. Unless you want to see only the traces for the past few frames, use an endless trace buffer (`flutter run --endless-trace-buffer` turns on an endless trace buffer).
Also, make sure to run your application with the `--trace-skia` flag.
## Debugging iOS builds with Xcode
Building with `flutter --local-engine` will set a `LOCAL_ENGINE` Xcode build setting in your Flutter application's `ios/Flutter/Generated.xcconfig` file. This will be set until you run `flutter run` again with either a different `--local-engine` option, or with none at all (which will unset it).
You can speed up your workflow by adding the `--config-only` flag to set up the Xcode build settings and plugins, but not compile the app. For example:
```bash
flutter build ios --local-engine ios_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt --config-only
```
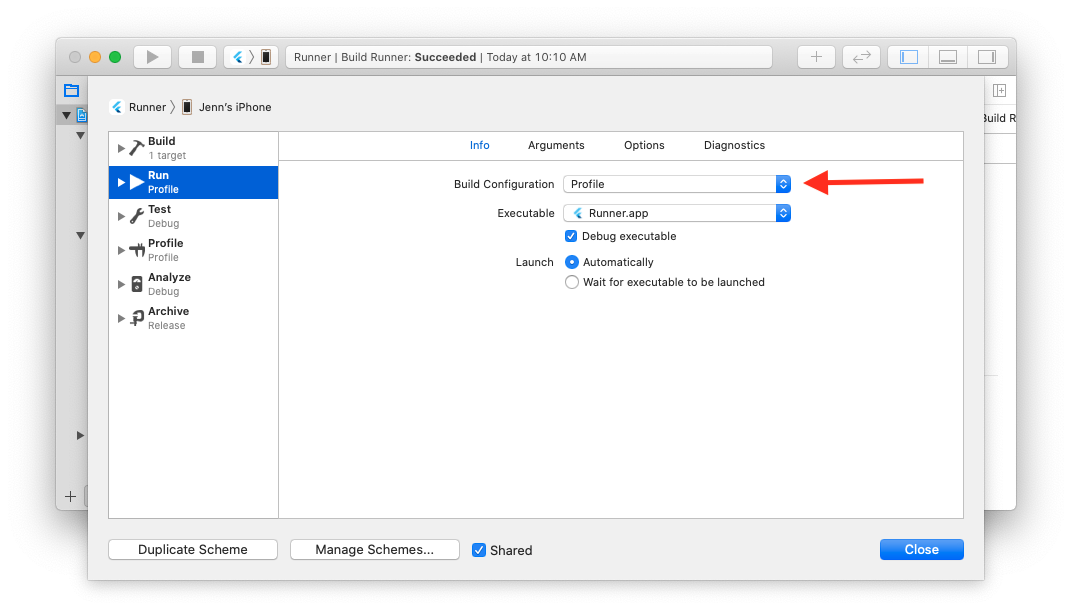
To start debugging, open your Flutter app `ios/Runner.xcworkspace` file in Xcode. Ensure **Product > Scheme > Edit Scheme > Run > Build Configuration** matches your engine runtime mode (defaults to `Debug`).
 Add an engine symbol breakpoint via **Debug > Breakpoints > Create Symbolic Breakpoint...**. The **Symbol** field should be the engine symbol you're interested in, like `-[FlutterEngine runWithEntrypoint:]` (note the `-[` prefix has no space).
You can also set a breakpoint directly with [lldb](https://lldb.llvm.org/tutorial.html) by expanding **Flutter > Runner** in the Runner Project Navigator. Put a breakpoint in `AppDelegate.swift`'s `application(didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` (Swift project) or `main.m`'s `main()` (Objective-C project) and start the application by clicking the Run button (CMD + R). Then, set your desired breakpoint in the engine in `lldb` via `breakpoint set -...`.
### Googlers using RBE
You need to tell Xcode where your Flutter Engine sources are located. You can do this using an LLDB Init file. Place one in your home directory named `~/.lldbinit`. The contents of the file should be (fixup the path as necessary):
```
settings set target.source-map "flutter/" "/path/to/engine/src/flutter/"
```
## Debugging Android builds with gdb
See https://github.com/flutter/engine/blob/main/sky/tools/flutter_gdb#L13
## Debugging native engine code on Android with Android Studio
1. Build the local engine with the `--no-stripped` flag.
2. Decide on a Flutter app that you with to debug and run it with `flutter run` and the local engine flags. i.e.: `--debug --local-engine-src-path path/to/my/engine/src --local-engine=android_debug_unopt_arm64`
3. Open Android Studio and use `File > Profile or Debug APK`. The location of the debug build APK should be `build/app/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk` under the Flutter app project.
4. To attach the debugger, use `Run > Attach Debugger to Android Process`. For "Use Android Debugger Settings from" choose `[Use default settings]`, and for "Debug Type" choose `Native Only`.
5. Once attached, you can use Android Studio to open local engine C++ source files and set breakpoints.
## Debugging Windows builds with Visual Studio
Compiling the engine creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the engine:
1. Launch your Flutter app using a locally built engine `flutter run -d windows --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the engine's solution file `.\out\host_debug_unopt\all.sln`
3. Open `Debug` > `Attach to Process...` (or press `CTRL+ALT+P`)
4. Choose your Flutter app using either `Select Window`, or, the list of available processes.
5. Press the `Attach` button
Building a Flutter app also creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the
engine, your app's runner, and your app's plugins:
1. Build your Flutter app using a locally built engine using `flutter build windows --debug --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the Flutter app's `.\build\windows\.sln`
3. In the `Solution Explorer` pane, right click the project whose name matches your app, and select `Set as Startup Project`

4. Now run your app by pressing `F5` or `DEBUG` > `Start Debugging`. This will launch your app with Visual Studio's debugger attached.
Read this guide to [learn how to debug C++ using Visual Studio](https://learn.microsoft.com/visualstudio/debugger/getting-started-with-the-debugger-cpp?view=vs-2022).
## Debugging with gdb on Linux
Once you have built the engine, you'll find the unstripped libraries in `out/host_debug_unopt/lib.unstripped`, and the executables in `out/host_debug_unopt/exe.unstripped`.
So, for instance, to run the unit tests under the debugger you would execute:
```shell
flutter/tools/gn --runtime-mode=debug --unoptimized
ninja -C out/host_debug_unopt
gdb out/host_debug_unopt/exe.unstripped/flutter_linux_unittests
```
And then debug the test normally using GDB commands.
To debug a Flutter app using GDB, the stripped flutter engine GTK library in the built application needs to be replaced with the unstripped one in the engine build output directory.
First, in your Flutter project, build your Flutter app using the local engine:
```shell
flutter build linux --debug --local-engine=host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host=host_debug_unopt lib/main.dart
```
Then, replace the library in your Flutter application's build directory: `build/linux/x64/debug/bundle/lib/libflutter_linux_gtk.so` with a copy or symbolic link to the engine build's output file `out/host_debug_unopt/lib.unstripped/libflutter_linux_gtk.so`.
Then you can open it in the debugger with:
```shell
gdb build/linux/x64/debug/bundle/your_app_name
```
Note that this won't help you debug the Dart portion of the app: this is just for debugging the engine code. If you need to simultaneously debug the Dart portion, you can connect to the observatory port given when you run the app in `gdb`.
## Logging in the engine
Flutter tool will by default parse out any non-error output from the engine. Error logs will be displayed. Logging is handled though the FML library's `logging.h`.
Add an engine symbol breakpoint via **Debug > Breakpoints > Create Symbolic Breakpoint...**. The **Symbol** field should be the engine symbol you're interested in, like `-[FlutterEngine runWithEntrypoint:]` (note the `-[` prefix has no space).
You can also set a breakpoint directly with [lldb](https://lldb.llvm.org/tutorial.html) by expanding **Flutter > Runner** in the Runner Project Navigator. Put a breakpoint in `AppDelegate.swift`'s `application(didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` (Swift project) or `main.m`'s `main()` (Objective-C project) and start the application by clicking the Run button (CMD + R). Then, set your desired breakpoint in the engine in `lldb` via `breakpoint set -...`.
### Googlers using RBE
You need to tell Xcode where your Flutter Engine sources are located. You can do this using an LLDB Init file. Place one in your home directory named `~/.lldbinit`. The contents of the file should be (fixup the path as necessary):
```
settings set target.source-map "flutter/" "/path/to/engine/src/flutter/"
```
## Debugging Android builds with gdb
See https://github.com/flutter/engine/blob/main/sky/tools/flutter_gdb#L13
## Debugging native engine code on Android with Android Studio
1. Build the local engine with the `--no-stripped` flag.
2. Decide on a Flutter app that you with to debug and run it with `flutter run` and the local engine flags. i.e.: `--debug --local-engine-src-path path/to/my/engine/src --local-engine=android_debug_unopt_arm64`
3. Open Android Studio and use `File > Profile or Debug APK`. The location of the debug build APK should be `build/app/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk` under the Flutter app project.
4. To attach the debugger, use `Run > Attach Debugger to Android Process`. For "Use Android Debugger Settings from" choose `[Use default settings]`, and for "Debug Type" choose `Native Only`.
5. Once attached, you can use Android Studio to open local engine C++ source files and set breakpoints.
## Debugging Windows builds with Visual Studio
Compiling the engine creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the engine:
1. Launch your Flutter app using a locally built engine `flutter run -d windows --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the engine's solution file `.\out\host_debug_unopt\all.sln`
3. Open `Debug` > `Attach to Process...` (or press `CTRL+ALT+P`)
4. Choose your Flutter app using either `Select Window`, or, the list of available processes.
5. Press the `Attach` button
Building a Flutter app also creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the
engine, your app's runner, and your app's plugins:
1. Build your Flutter app using a locally built engine using `flutter build windows --debug --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the Flutter app's `.\build\windows\.sln`
3. In the `Solution Explorer` pane, right click the project whose name matches your app, and select `Set as Startup Project`

4. Now run your app by pressing `F5` or `DEBUG` > `Start Debugging`. This will launch your app with Visual Studio's debugger attached.
Read this guide to [learn how to debug C++ using Visual Studio](https://learn.microsoft.com/visualstudio/debugger/getting-started-with-the-debugger-cpp?view=vs-2022).
## Debugging with gdb on Linux
Once you have built the engine, you'll find the unstripped libraries in `out/host_debug_unopt/lib.unstripped`, and the executables in `out/host_debug_unopt/exe.unstripped`.
So, for instance, to run the unit tests under the debugger you would execute:
```shell
flutter/tools/gn --runtime-mode=debug --unoptimized
ninja -C out/host_debug_unopt
gdb out/host_debug_unopt/exe.unstripped/flutter_linux_unittests
```
And then debug the test normally using GDB commands.
To debug a Flutter app using GDB, the stripped flutter engine GTK library in the built application needs to be replaced with the unstripped one in the engine build output directory.
First, in your Flutter project, build your Flutter app using the local engine:
```shell
flutter build linux --debug --local-engine=host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host=host_debug_unopt lib/main.dart
```
Then, replace the library in your Flutter application's build directory: `build/linux/x64/debug/bundle/lib/libflutter_linux_gtk.so` with a copy or symbolic link to the engine build's output file `out/host_debug_unopt/lib.unstripped/libflutter_linux_gtk.so`.
Then you can open it in the debugger with:
```shell
gdb build/linux/x64/debug/bundle/your_app_name
```
Note that this won't help you debug the Dart portion of the app: this is just for debugging the engine code. If you need to simultaneously debug the Dart portion, you can connect to the observatory port given when you run the app in `gdb`.
## Logging in the engine
Flutter tool will by default parse out any non-error output from the engine. Error logs will be displayed. Logging is handled though the FML library's `logging.h`.
 Add an engine symbol breakpoint via **Debug > Breakpoints > Create Symbolic Breakpoint...**. The **Symbol** field should be the engine symbol you're interested in, like `-[FlutterEngine runWithEntrypoint:]` (note the `-[` prefix has no space).
You can also set a breakpoint directly with [lldb](https://lldb.llvm.org/tutorial.html) by expanding **Flutter > Runner** in the Runner Project Navigator. Put a breakpoint in `AppDelegate.swift`'s `application(didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` (Swift project) or `main.m`'s `main()` (Objective-C project) and start the application by clicking the Run button (CMD + R). Then, set your desired breakpoint in the engine in `lldb` via `breakpoint set -...`.
### Googlers using RBE
You need to tell Xcode where your Flutter Engine sources are located. You can do this using an LLDB Init file. Place one in your home directory named `~/.lldbinit`. The contents of the file should be (fixup the path as necessary):
```
settings set target.source-map "flutter/" "/path/to/engine/src/flutter/"
```
## Debugging Android builds with gdb
See https://github.com/flutter/engine/blob/main/sky/tools/flutter_gdb#L13
## Debugging native engine code on Android with Android Studio
1. Build the local engine with the `--no-stripped` flag.
2. Decide on a Flutter app that you with to debug and run it with `flutter run` and the local engine flags. i.e.: `--debug --local-engine-src-path path/to/my/engine/src --local-engine=android_debug_unopt_arm64`
3. Open Android Studio and use `File > Profile or Debug APK`. The location of the debug build APK should be `build/app/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk` under the Flutter app project.
4. To attach the debugger, use `Run > Attach Debugger to Android Process`. For "Use Android Debugger Settings from" choose `[Use default settings]`, and for "Debug Type" choose `Native Only`.
5. Once attached, you can use Android Studio to open local engine C++ source files and set breakpoints.
## Debugging Windows builds with Visual Studio
Compiling the engine creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the engine:
1. Launch your Flutter app using a locally built engine `flutter run -d windows --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the engine's solution file `.\out\host_debug_unopt\all.sln`
3. Open `Debug` > `Attach to Process...` (or press `CTRL+ALT+P`)
4. Choose your Flutter app using either `Select Window`, or, the list of available processes.
5. Press the `Attach` button
Building a Flutter app also creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the
engine, your app's runner, and your app's plugins:
1. Build your Flutter app using a locally built engine using `flutter build windows --debug --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the Flutter app's `.\build\windows\
Add an engine symbol breakpoint via **Debug > Breakpoints > Create Symbolic Breakpoint...**. The **Symbol** field should be the engine symbol you're interested in, like `-[FlutterEngine runWithEntrypoint:]` (note the `-[` prefix has no space).
You can also set a breakpoint directly with [lldb](https://lldb.llvm.org/tutorial.html) by expanding **Flutter > Runner** in the Runner Project Navigator. Put a breakpoint in `AppDelegate.swift`'s `application(didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` (Swift project) or `main.m`'s `main()` (Objective-C project) and start the application by clicking the Run button (CMD + R). Then, set your desired breakpoint in the engine in `lldb` via `breakpoint set -...`.
### Googlers using RBE
You need to tell Xcode where your Flutter Engine sources are located. You can do this using an LLDB Init file. Place one in your home directory named `~/.lldbinit`. The contents of the file should be (fixup the path as necessary):
```
settings set target.source-map "flutter/" "/path/to/engine/src/flutter/"
```
## Debugging Android builds with gdb
See https://github.com/flutter/engine/blob/main/sky/tools/flutter_gdb#L13
## Debugging native engine code on Android with Android Studio
1. Build the local engine with the `--no-stripped` flag.
2. Decide on a Flutter app that you with to debug and run it with `flutter run` and the local engine flags. i.e.: `--debug --local-engine-src-path path/to/my/engine/src --local-engine=android_debug_unopt_arm64`
3. Open Android Studio and use `File > Profile or Debug APK`. The location of the debug build APK should be `build/app/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk` under the Flutter app project.
4. To attach the debugger, use `Run > Attach Debugger to Android Process`. For "Use Android Debugger Settings from" choose `[Use default settings]`, and for "Debug Type" choose `Native Only`.
5. Once attached, you can use Android Studio to open local engine C++ source files and set breakpoints.
## Debugging Windows builds with Visual Studio
Compiling the engine creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the engine:
1. Launch your Flutter app using a locally built engine `flutter run -d windows --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the engine's solution file `.\out\host_debug_unopt\all.sln`
3. Open `Debug` > `Attach to Process...` (or press `CTRL+ALT+P`)
4. Choose your Flutter app using either `Select Window`, or, the list of available processes.
5. Press the `Attach` button
Building a Flutter app also creates a Visual Studio solution file. You can use it to debug the
engine, your app's runner, and your app's plugins:
1. Build your Flutter app using a locally built engine using `flutter build windows --debug --local-engine host_debug_unopt --local-engine-host host_debug_unopt`
2. Using Visual Studio, open the Flutter app's `.\build\windows\